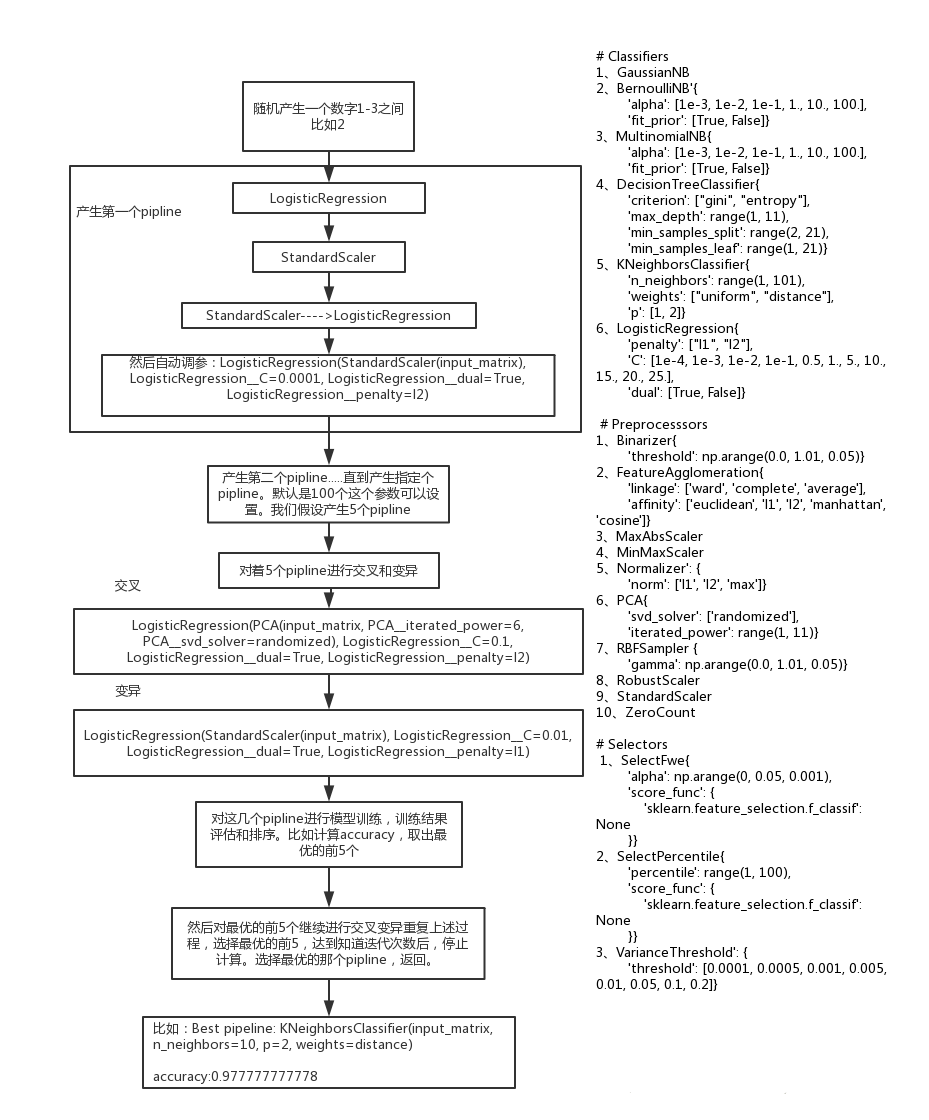
TPOT的涉及到的建模过程,以TPOT light为例主要有3块:Classifiers、Preprocesssors、Selectors,TPOT的遗传算法优化是以pipeline为基础的,也就是说pipeline就相当于基因序列。通过构建初始pipeline,再经过遗传算法中的交叉、变异最终生成符合条件的模型效果较好的pipeline。我们从最优的那一代中选取其中建模效果最好的pipeline即可,TPOT是基于scikit-learn框架的,它本身不去实现我们常用的分类回归等算法。而是通过遗传算法优化pipeline。也就是从中选出最优的数据处理、特征选择、分类算法的组合。
一个简单的TPOT的使用实例:
1 | #!/usr/local/bin/python |
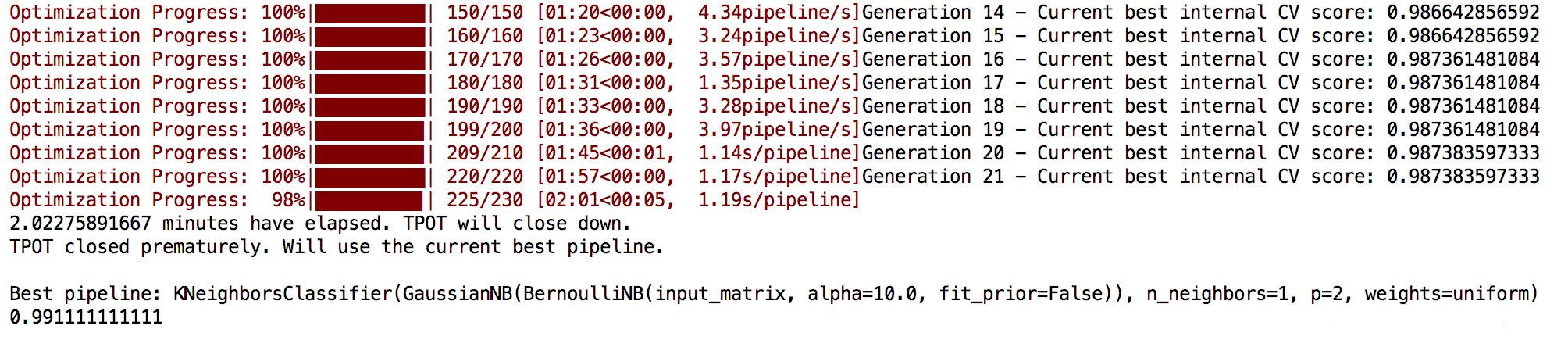
运行结果如下:
部分核心源码解读
1、初始群体的生成
这段代码可以看出,pipeline的构建是通过生成不同深度的树类构建初始pipeline的,大致过程是先确定树的深度,从Classifiers中选择一个分类器放入树的顶端,接下来构建分类器的参数,以上均为随机选取。如果树的深度大于1,则还需要从Preprocesssors、Selectors中选择算子加入到pipeline中,还要进行参数初始化。
1 |
|
2、适应性值评估检测
1 | def _evaluate_individuals(self, individuals, features, target, sample_weight=None, groups=None): |
3、变异
变异主要是增加pipeline的内容或更换其中的参数。
1 | def _random_mutation_operator(self, individual, allow_shrink=True): |
4、交叉
选取两个pipeline,对里面的内容进行互换,但是两个pipeline的primitive要相同。
1 | def pick_two_individuals_eligible_for_crossover(population): |
TPOT设置了一个阈值来决定是交叉还是变异,默认情况下变异的概率为0.9,交叉的概率为0.1.我们可以修改这个阈值。
具体的pipeline变换如下:
默认的种群数量为100,为了看源码方便,改为了5个种群数。交叉变异的概率各为0.5.
1 | tpot = TPOTClassifier(verbosity=2, max_time_mins=2,config_dict="TPOT light",population_size=5,mutation_rate=0.5,crossover_rate=0.5) |
初始种群为5个pipeline,分别为:
1 | 0 = {Individual} KNeighborsClassifier(PCA(input_matrix, PCA__iterated_power=6, PCA__svd_solver=randomized), KNeighborsClassifier__n_neighbors=79, KNeighborsClassifier__p=1, KNeighborsClassifier__weights=distance) |
经过第一轮交叉、变异,结果为:
1 | 0 = {Individual} LogisticRegression(PCA(input_matrix, PCA__iterated_power=6, PCA__svd_solver=randomized), LogisticRegression__C=0.1, LogisticRegression__dual=True, LogisticRegression__penalty=l2) |
然后对这几个pipeline进行打分评估,和上一轮pipeline一起选出score最高的前5个。
进入下一轮迭代。最后产生5个pipeline,打分,从中选出最优的那个:
1 | Best pipeline: KNeighborsClassifier(input_matrix, n_neighbors=10, p=2, weights=distance) |
流程举例如下(具体流程和TPOT代码本身略有区别,但是不影响对遗传算法自动化建模的理解)