TPOT—一个自动化的Python机器学习工具

TPOT全称是基于树的pipeline优化工具(Tree-based Pipeline Optimization Tool),这是一个非常棒Python自动机器学习工具,使用遗传编程优化机器学习pipeline。
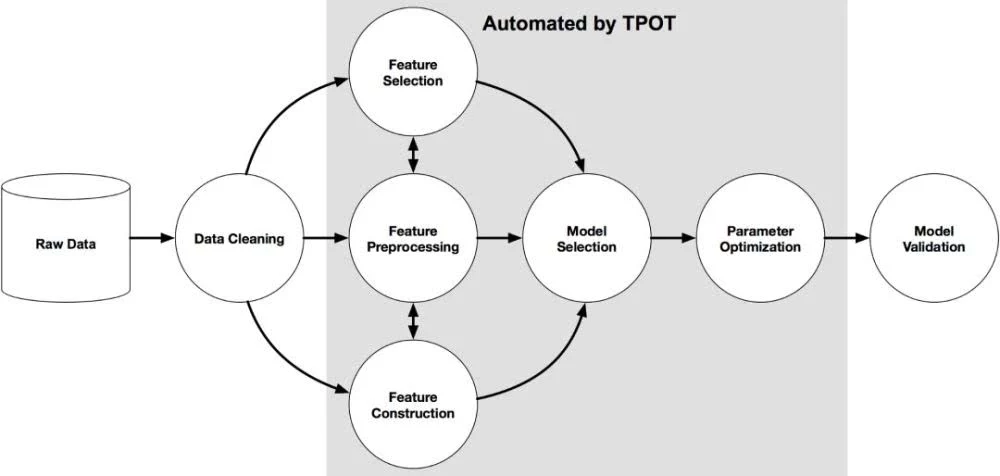
TPOT可以自动化许多东西,包括生命特性选择、模型选择、特性构建等等。如果你是Python机器学习者,很幸运,TPOT是构建在Scikit-learn之上的,所以它生成的所有代码看起来应该很熟悉。
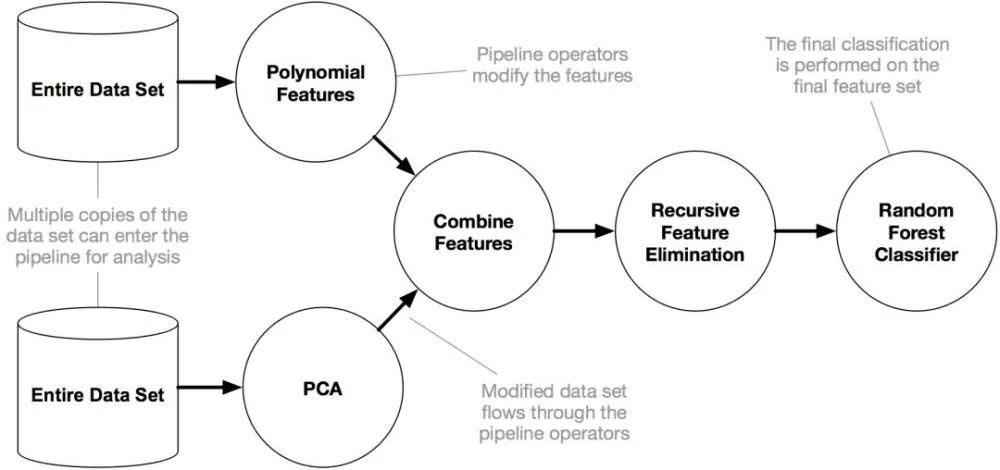
它的作用是通过智能地探索数千种可能的pipeline来自动化机器学习中最繁琐的部分,找到最适合你的数据的pipeline,然后为你提供最佳的 Python 代码。
它的工作原理如下:
1 安装
安装TPOT,可参考以下文档:
http://epistasislab.github.io/tpot/installing/
2 使用
2.1 TPOT代码
TPOT的接口,与scikit-learn很类似。
TPOT可以像任何常规的Python模块一样导入:1
from tpot import TPOTClassifier
然后创建一个TPOT实例如下:1
pipeline_optimizer = TPOTClassifier()
当然,TPOTRegressor()也可以。
一些带有定制TPOT参数的示例代码可能如下:1
pipeline_optimizer = TPOTClassifier(generations=5, population_size=20, cv=5, random_state=42, verbosity=2)
现在,可以利用fit函数来寻找最优的管道:
1 | pipeline_optimizer.fit(X_train, y_train) |
fit函数初始化了遗传算法,以找到基于平均k倍交叉验证的最高评分管道,然后对整个提供的样本进行训练,TPOT实例可以作为一个合适的模型使用。
然后,可以使用score函数来评估测试集中的最终管道:1
print(pipeline_optimizer.score(X_test, y_test))
最后,可以把TPOT将相应的Python代码导出到文本文件中:1
pipeline_optimizer.export('tpot_exported_pipeline.py')
下面是一个完整的示例脚本,使用TPOT优化管道,对其进行评分,并将最好的管道导出到文件中。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11from tpot import TPOTClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
digits = load_digits()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(digits.data, digits.target,train_size=0.75, test_size=0.25)
pipeline_optimizer = TPOTClassifier(generations=5, population_size=20, cv=5,random_state=42, verbosity=2)
pipeline_optimizer.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(pipeline_optimizer.score(X_test, y_test))
pipeline_optimizer.export('tpot_exported_pipeline.py')
2.2 TPOT命令行
TPOT可以通过命令行导入使用1
tpot /path_to/data_file.csv
命令行导入使用TPOT的示例代码如下:1
tpot data/mnist.csv -is , -target class -o tpot_exported_pipeline.py -g 5 -p 20 -cv 5 -s 42 -v 2
2.3 评估函数
TPOT允许自定义评分函数,具体例子可以参考Scoring Functions
2.4 内置TPOT配置
TPOT提供了一些默认的操作符和参数配置,它可以很好地优化机器学习管道。下面是TPOT当前内置配置的列表。它有4种:
- Default TPOT:默认的参数,在一些大数据集上可能需要较长时间。
- TPOT light:与Default TPOT相比,使用了更简单、快速运行的操作符,因此TPOT light对于查找用于分类或回归问题的快速简单的管道非常有用。
- TPOT MDR:专门用于全基因组关联研究(GWAS)
- TPOT sparse:带有one-hot编码,且支持稀疏矩阵。
如果要使用这些配置只需将配置的字符串名称传递给config_dict 参数。示例代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11from tpot import TPOTClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
digits = load_digits()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(digits.data, digits.target,train_size=0.75, test_size=0.25)
tpot = TPOTClassifier(generations=5, population_size=20, verbosity=2,config_dict='TPOT light')
tpot.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(tpot.score(X_test, y_test))
tpot.export('tpot_mnist_pipeline.py')2.5 定制TPOT的操作符和参数
除了TPOT所带来的默认配置之外,在某些情况下,限制TPOT所考虑的算法和参数是很有用的(用于减少寻优的时间等)。出于这个原因,TPOT允许用户为TPOT提供其操作符和参数的自定义配置。
自定义TPOT配置必须采用嵌套字典格式,举一个例子:这样,TPOT寻找最优的pipeline,就只会在tpot_config中寻找了,无疑大大减少了时间复杂度,不过准确性可能会下降。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27from tpot import TPOTClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
digits = load_digits()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(digits.data, digits.target,train_size=0.75, test_size=0.25)
tpot_config = {
'sklearn.naive_bayes.GaussianNB': {
},
'sklearn.naive_bayes.BernoulliNB': {
'alpha': [1e-3, 1e-2, 1e-1, 1., 10., 100.],
'fit_prior': [True, False]
},
'sklearn.naive_bayes.MultinomialNB': {
'alpha': [1e-3, 1e-2, 1e-1, 1., 10., 100.],
'fit_prior': [True, False]
}
}
tpot = TPOTClassifier(generations=5, population_size=20, verbosity=2,
config_dict=tpot_config)
tpot.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(tpot.score(X_test, y_test))
tpot.export('tpot_mnist_pipeline.py')2.6 Note
搜索整个管道空间是特别耗时的。认识到原因是必要的,在默认的TPOT参数下(100 generations with 100 population size),TPOT将在完成前评估1万个管道配置。考虑一个网格搜索1万个超参数组合用于机器学习算法以及网格搜索需要多长时间。用10倍的交叉验证来评估这1万个模型,这意味着大约有10万个模型在一个网格搜索的训练数据中被匹配和评估。这是一个耗时的过程,即使对于像决策树这样的简单模型也是如此。
典型的TPOT运行将需要数小时到数天才能完成(除非是一个小数据集),但是可以中断运行,并看到目前为止最好的结果。TPOT还提供warm_start参数,可以从中断的地方重新启动之前运行的TPOT。
3. TPOT API
以TPOTRegressor为例,分类问题一样。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13class tpot.TPOTRegressor(generations=100, population_size=100,
offspring_size=None, mutation_rate=0.9,
crossover_rate=0.1,
scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', cv=5,
subsample=1.0, n_jobs=1,
max_time_mins=None, max_eval_time_mins=5,
random_state=None, config_dict=None,
warm_start=False,
memory=None,
periodic_checkpoint_folder=None,
early_stop=None,
verbosity=0,
disable_update_check=False)
在默认情况下,TPOTRegressor将搜索广泛的监督的回归模型,包括预处理,特征选择,学习器和它们的超参数。当然,TPOTRegressor可以完全自己定制。
参数,属性和方法的详情可以参考如下
下面列出主要的参数和方法:
参数:
- generations: int, optional (default=100),运行管道优化过程的迭代次数。一定是正数,默认是100。一般来说,值越大,性能越好。
TPOT将评估population_size+generations×offspring_size的规模。
population_size: int, optional (default=100),在每一代遗传中保留的个体数。一定是正数。一般来说,值越大,性能越好。
offspring_size: int, optional (default=100),在每一次遗传过程中产生的后代数量。一定是正数。
- mutation_rate: float, optional (default=0.9),变异率,采用默认值即可。
- crossover_rate: float, optional (default=0.1),交叉率,采用默认值即可。
- scoring: string or callable, optional (default=’neg_mean_squared_error’),回归问题中用于评估给定管道的质量的函数。可以使用以下内置评分函数: ‘neg_median_absolute_error’, ‘neg_mean_absolute_error’, ‘neg_mean_squared_error’, ‘r2’
- cv: int, cross-validation generator, or an iterable, optional (default=5)
- subsample: float, optional (default=1.0),在TPOT优化过程中使用的训练样本的比例。必须在0到1之间。
- n_jobs: integer, optional (default=1)
- max_time_mins: integer or None, optional (default=None),TPOT需要多少分钟来优化管道。
- max_eval_time_mins: integer, optional (default=5),TPOT需要多少分钟来评估一个管道。
- random_state: integer or None, optional (default=None),使用这个参数来确保TPOT每次运行时都会有相同的结果。
- config_dict: Python dictionary, string, or None, optional (default=None),用于定制TPOT在优化过程中搜索的操作符和参数的配置字典。
- warm_start: boolean, optional (default=False),表明TPOT实例是否会重用以前调用fit()的入口。
- early_stop: integer, optional (default: None)
- verbosity: integer, optional (default=0),
0,TPOT将不会打印任何东西,
1,将打印很少的信息,
2,TPOT将会打印更多的信息并提供一个进度条
3,TPOT将打印所有内容,并提供一个进度条
方法:
- fit(features, target, sample_weight=None, groups=None),在给定的训练数据上运行TPOT优化过程。
- predict(features),使用优化的管道来预测测试集的目标值。
- score(testing_features, testing_target),使用用户指定的评分函数在给定的测试数据上返回优化的管道的得分。
- export(output_file_name),将优化的管道导出为Python代码。
4.实例
例4.1
数据集地址:https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/breast-cancer-wisconsin/
使用的数据集:breast-cancer-wisconsin.data
直接把数据全选复制到txt中,然后直接改文件后缀为csv,把文件转换为csv格式。并加上属性名
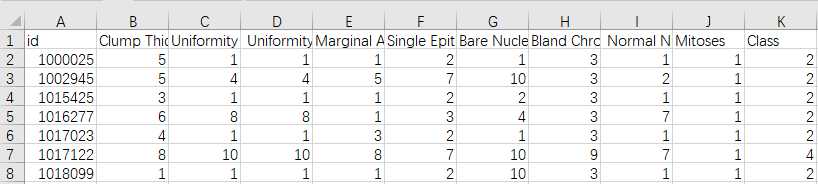
程序:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31#-*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
'''
使用TPOT自动选择scikit-learn机器学习模型和参数
'''
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import model_selection
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from tpot import TPOTClassifier
inputfile='C:/Users/bryce/Desktop/breast-cancer-wisconsin.data.csv'
def main():
df=pd.read_csv(inputfile)
#print(df.head())
df.replace('?',np.nan,inplace=True)
df.dropna(inplace=True)
df.drop(['id'],1,inplace=True)
#print(df.head())
df['Bare Nuclei'] = df['Bare Nuclei'].astype(int)
X=np.array(df.drop(['Class'],1))
Y=np.array(df['Class'])
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=model_selection.train_test_split(X,Y,test_size=0.2)
tpot=TPOTClassifier(generations=6,verbosity=2)
tpot.fit(x_train,y_train)
tpot.score(x_test,y_test)
tpot.export('pipeline.py')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
运行结果如下:
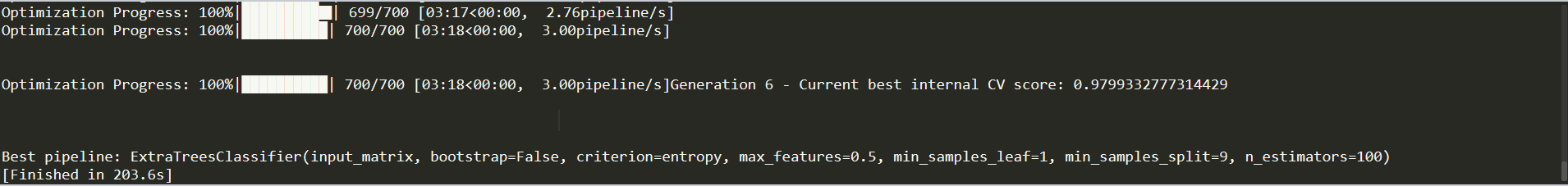
可以看到运行的最优结果是随机森林算法,并给出具体的参数。
再运行一下随机森林算法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36#-*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
'''
使用TPOT自动选择scikit-learn机器学习模型和参数
'''
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import model_selection
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from tpot import TPOTClassifier
inputfile='C:/Users/bryce/Desktop/breast-cancer-wisconsin.data.csv'
def main():
df=pd.read_csv(inputfile)
#print(df.head())
df.replace('?',np.nan,inplace=True)
df.dropna(inplace=True)
df.drop(['id'],1,inplace=True)
df['Bare Nuclei'] = df['Bare Nuclei'].astype(int)
#print(df.head())
X=np.array(df.drop(['Class'],1))
Y=np.array(df['Class'])
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=model_selection.train_test_split(X,Y,test_size=0.2)
# tpot=TPOTClassifier(generations=6,verbosity=2)
# tpot.fit(x_train,y_train)
# tpot.score(x_test,y_test)
# tpot.export('pipeline.py')
rfc=RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, criterion='entropy', max_features=0.05, min_samples_leaf=3, min_samples_split=16, n_estimators=100)
rfc.fit(x_train,y_train)
accuracy=rfc.score(x_test,y_test)
print("accuracy:%s"%accuracy)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
运行结果如下:
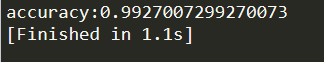
例4.2
数据集:sklearn自带的波士顿房价数据集
