priority_queue本质是一个堆。
1.头文件是#include<queue>
2.关于priority_queue中元素的比较
模板申明带3个参数:priority_queue
Container必须是用数组实现的容器,比如vector,deque等等,但不能用 list。STL里面默认用的是vector。
基本操作有:
empty( ) //判断一个队列是否为空
pop( ) //删除队顶元素
top( ) //返回优先队列的队顶元素
push( ) //加入一个元素
size( ) //返回优先队列中拥有的元素个数
优先队列的时间复杂度为O(logn),n为队列中元素的个数,其存取都需要时间。
在默认的优先队列中,优先级最高的先出队。默认的int类型的优先队列中先出队的为队列中较大的数。
2.1 第一种用法(默认从大到小排序):
如果元素是pair的话,先按照pair的first元素降序,first元素相等时,再按照second元素降序:1
priority_queue<int> q1;//默认从大到小排序,整数中元素大的优先级高
1 |
|
结果:

2.2 第二种用法(从小到大排序):
1 | priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q1; |
1 |
|
结果:

2.3 第三种用法:自定义排序规则
对于自定义类型,则必须重载operator<或者重写仿函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
using namespace std;
int tmp[100];
struct cmp1{
bool operator()(int x,int y)
{
return x>y;//小的优先级高 ,从小到大排
}
};
struct cmp2{
bool operator()(const int x,const int y)
{
return tmp[x]>tmp[y];
}
};
struct node{
int x,y;
friend bool operator<(node a,node b)
{
return a.x>b.x;//按x从小到大排
}
};
priority_queue<int>q1;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,cmp1>q2;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,cmp2>q3;
priority_queue<node>q4;
int main()
{
int i,j,k,m,n;
int x,y;
node a;
while(cin>>n)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a.y>>a.x;
q4.push(a);
}
cout<<endl;
while(!q4.empty())
{
cout<<q4.top().y<<" "<<q4.top().x<<" "<<endl;
q4.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
int t;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>t;
q2.push(t);
}
while(!q2.empty())
{
cout<<q2.top()<<endl;
q2.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果:
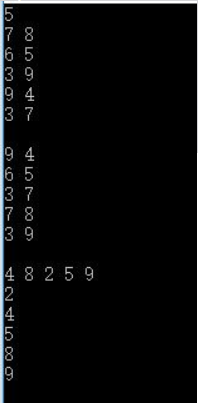
参考:
