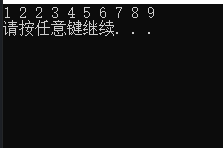
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| #include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int Partition(vector<int> & nums, int low, int high)
{
int pivot = nums[low];
while (low<high)
{
while(low<high && nums[high]>=pivot)
{
high--;
}
nums[low] = nums[high];
while(low<high && nums[low]<pivot)
{
low++;
}
nums[high] = nums[low];
}
nums[low] = pivot;
return low;
}
void quickSort(vector<int> &nums, int start, int end)
{
stack<int> s;
if (start<end)
{
int pivot = Partition(nums,start,end);
if (pivot-1>start)
{
s.push(start);
s.push(pivot-1);
}
if (pivot+1<end)
{
s.push(pivot+1);
s.push(end);
}
while (!s.empty())
{
int r = s.top();
s.pop();
int l = s.top();
s.pop();
pivot = Partition(nums,l,r);
if(pivot-1>l)
{
s.push(l);
s.push(pivot-1);
}
if (pivot+1<r)
{
s.push(pivot+1);
s.push(r);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
vector<int> nums = {2,5,6,1,2,7,8,3,4,9};
int n = nums.size();
quickSort(nums,0,n-1);
for (int num: nums)
{
cout << num << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|