Dijkstra算法
学习了一下关于Dijlstra最短路的算法,做一下总结,梳理一下思路。
求最短路算法一般分为求单源最短路和多源汇最短路,思维导图如图所示: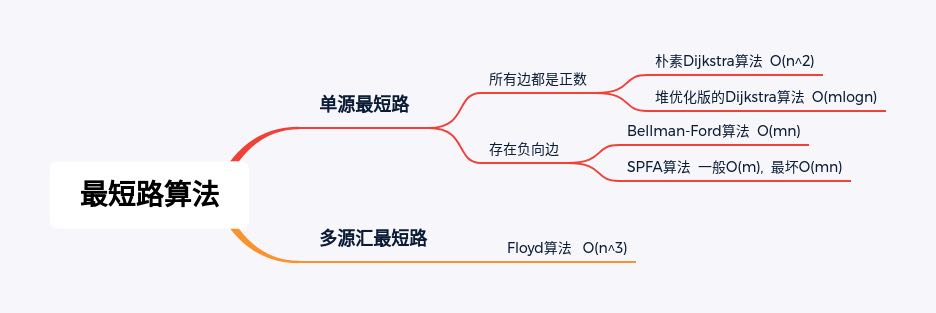
其中n表示节点数,m表示边数。
稠密图:m与n^2是一个级别的,用邻接矩阵来表示。
稀疏图:m远远小于n^2,用邻接表来表示,比邻接矩阵更节省空间
具体邻接矩阵和邻接表可以参考这篇文章图的邻接矩阵和邻接表的比较
朴素Dijkstra算法
给定一个n个点m条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环,所有边权均为正值。
请你求出1号点到n号点的最短距离,如果无法从1号点走到n号点,则输出-1。
输入格式
第一行包含整数n和m。
接下来m行每行包含三个整数x,y,z,表示存在一条从点x到点y的有向边,边长为z。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示1号点到n号点的最短距离。
如果路径不存在,则输出-1。
数据范围
1≤n≤500,
1≤m≤105,
图中涉及边长均不超过10000。
输入样例:1
2
3
43 3
1 2 2
2 3 1
1 3 4
输出样例:1
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
using namespace std;
const int N = 510;
int n, m;
int g[N][N]; //为稠密阵所以用邻接矩阵存储
bool st[N]; //用于在更新最短距离时 判断当前的点的最短距离是否确定 是否需要更新
int dist[N]; //用于存储每个点到起点的最短距离
int dijkstra(){
// 1. 初始化dist
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist)); //初始化距离 0x3f代表无限大
dist[1]=0; //第一个点到自身的距离为0
// 2. 循环遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int t = -1; //t存储当前访问的点
// t 不在s中,距离最近的点
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
//该步骤即寻找还未确定最短路的点中路径最短的点
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
// 通过上述操作当前我们的t代表就是剩余未确定最短路的点中 路径最短的点
// 同时该点的最短路径也已经确定我们将该点标记
st[t] = 1;
// 用t去更新其他所有点的距离
for (int j = 1; j <=n; ++j) {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
// 不存在到这条边的情况
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
cin >> m;
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof(g)); //求最短路所以每个点初始为无限大
while (m--) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
// a -> b 之间可能有多条边,只保留长度最短(权重最小)的那条边就可以了
g[a][b] = min(g[a][b],c);
}
int t =dijkstra();
cout << t << endl;
return 0;
}
堆优化Dijkstra算法
给定一个n个点m条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环,所有边权均为非负值。
请你求出1号点到n号点的最短距离,如果无法从1号点走到n号点,则输出-1。
输入格式
第一行包含整数n和m。
接下来m行每行包含三个整数x,y,z,表示存在一条从点x到点y的有向边,边长为z。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示1号点到n号点的最短距离。
如果路径不存在,则输出-1。
数据范围
1≤n,m≤1.5×105,
图中涉及边长均不小于0,且不超过10000。
输入样例:1
2
3
43 3
1 2 2
2 3 1
1 3 4
输出样例:1
3
// 使用邻接表实现(稀疏图用邻接表来实现)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6;
int n, m;
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> g;
vector<int> dist(N,1e9);
vector<int> st(N,0);
int dijkstra() {
dist[1] = 0;
priority_queue<pair<int,int>, vector<pair<int,int>>, greater<pair<int,int>>> q;
// 第一个是距离, 第二个参数是标号
q.push({0,1});
while(q.size()) {
auto p = q.top();
q.pop();
int curPos = p.second;
if (st[curPos]) continue;
st[curPos] = 1;
for (auto next : g[curPos]) {
int distance = next.second;
int nextPos = next.first;
if (distance + dist[curPos] < dist[nextPos]) {
dist[nextPos] = distance + dist[curPos];
q.push(make_pair(dist[nextPos], nextPos));
}
}
}
if (dist[n] == 1e9) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
g.resize(n+1);
while(m--) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
g[a].push_back({b,c});
}
int t = dijkstra();
cout << t << endl;
return 0;
}
总结
根据今天LC周赛,总结一套Dijkstra的模板,以后直接套这个模板就好
1 | struct DIJ { |
1 |
|
