RoaringBitMap原理 Roaring Bitmap实现的主要思路是将32位无符号整数(0~4294967295)分成高16位和低16位两部分。通过高 16 位找到该数据存储在哪个桶中(高 16 位可以划分 216 个桶),把剩余的低 16 位放入该桶对应的 Container 中。
每个桶都有对应的 Container,不同的 Container 存储方式不同。依据不同的场景,主要有 2 种不同的 Container,分别是 Array Container 和 Bitmap Container。Array Container 存放稀疏的数据,Bitmap Container 存放稠密的数据。若一个 Container 里面的元素数量小于 4096,使用 Array Container 来存储。当 Array Container 超过最大容量 4096 时,会转换为 Bitmap Container。
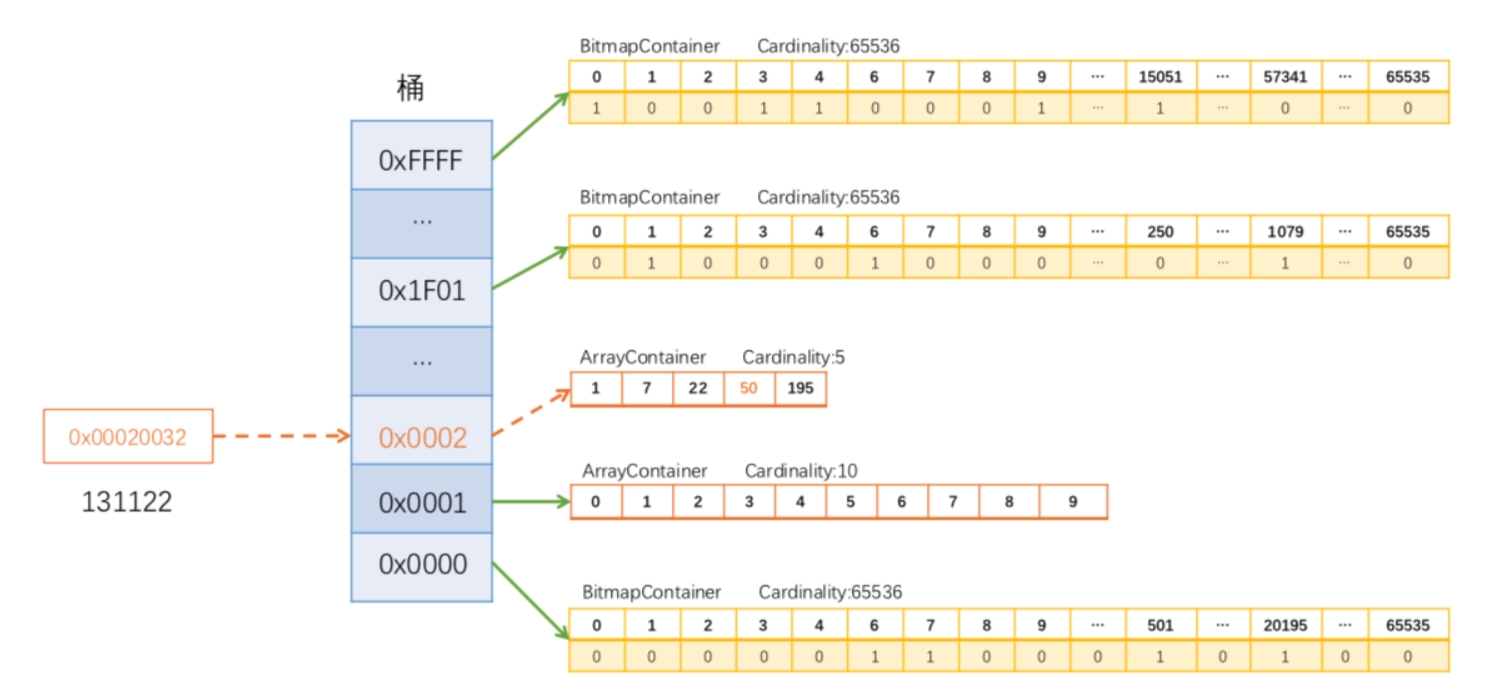
例1:0x00020032(十进制131122)放入一个 RBM 的过程如下图所示:
131122 的高 16 位是 0002,找到对应的桶 0x0002。在桶对应的 Container 中存储低 16 位,因为 Container 元素个数不足 4096,因此是一个 Array Container。低 16 位为 0032(十进制为50), 在 Array Container 中二分查找找到相应的位置插入即可(如上图50的位置)。相较于纯Bitmap 需要占用 16K (131122/8/1024) 内存来存储这个数,而这种存储实际只占用了4B(桶中占 2 B,Container中占 2 B,不考虑数组的初始容量)。
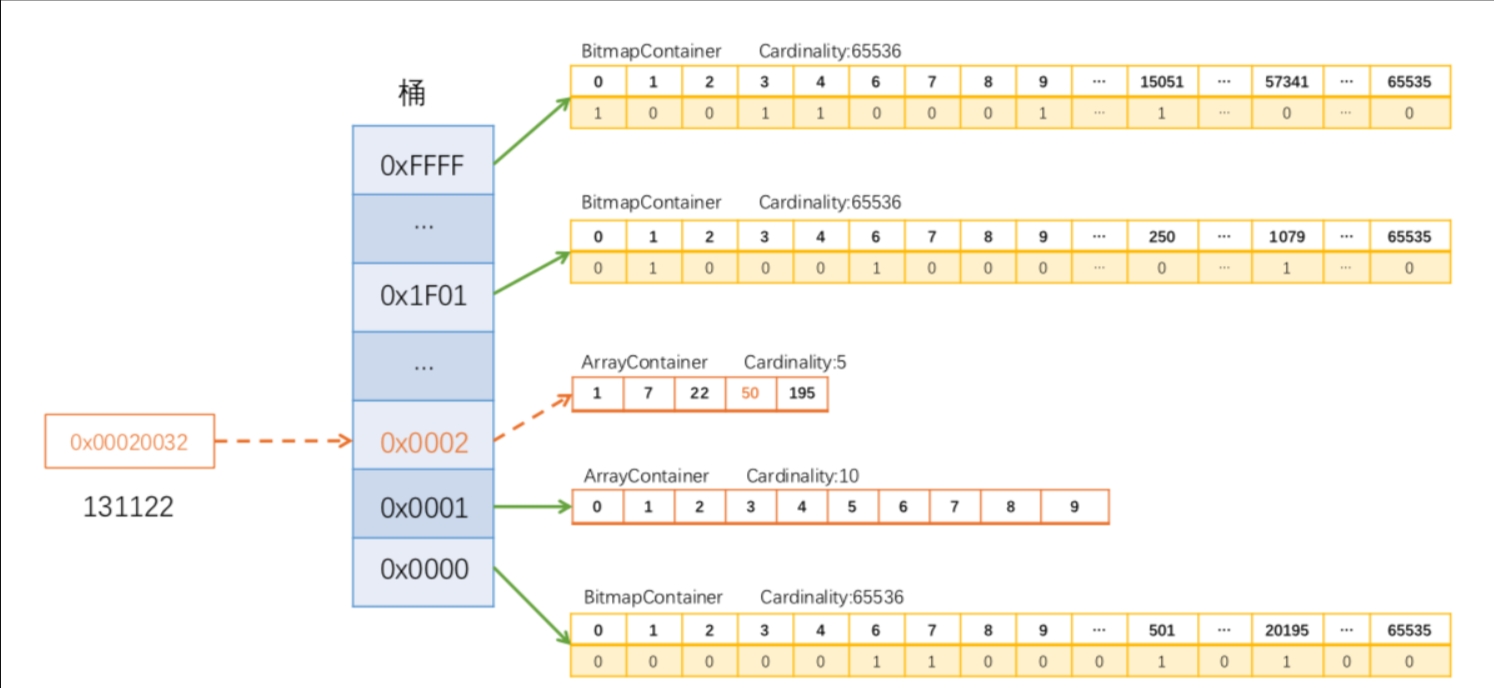
例2:0xFFFF3ACB(十进制4294916811)放入一个 RBM 的过程如下图所示:
4294916811 的高 16 位是 FFFF,找到对应的桶 0xFFFF。在桶对应的 Container 中存储低 16 位,因为 Container 中元素个数已经超过 4096,底层是一个 Bitmap Container。低 16 位为 3ACB(十进制为15051), 因此在 Bitmap Container 中通过下标直接寻址找到相应的位置,将其置为 1 即可(如上图15051的位置)。
由于每个 Bitmap Container 需要处理低 16 位数据,使用 Bitmap 来存储需要 8192 Bytes(2^16/8), 而一个 long 值占 8 个 Bytes,所以数组大小为 1024。因此一个 Bitmap Container 固定占用内存 8 KB。
RoaringBitmap数据结构 RoaringBitmap的基本构成如下:首先是一个RoaringArray,名字是high_low_container,该结构中存储了每个uint32整数的高16bit的索引keys以及具体存储数字的container。
RoaringArray 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 typedef struct roaring_bitmap_s { roaring_array_t high_low_container; } roaring_bitmap_t ; ... typedef struct roaring_array_s { int32_t size; int32_t allocation_size; ROARING_CONTAINER_T **containers; uint16_t *keys; uint8_t *typecodes; uint8_t flags; } roaring_array_t ;
roaring_array:每个RBM都包含了一个roaring_array,名字是high_low_container,该结构主要有下面几个重要属性:
keys:short数组,用来存储高16位作为索引
containers:container数组,用来存储低16位数据
typecodes:可理解为container type的数组,标识container的类型
size:可理解为rbm包含的key-value有效数量
PS:keys数组和containers数组是一一对应的,且keys永远保证有序,这是为了之后索引的二分查找
Containers Container用于存储低16位的数据,根据数据量以及疏密程度分为以下3个容器:
ArrayContainer
BitmapContainer
RunContainer
1、ArrayContainer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 enum { DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE = 4096 };STRUCT_CONTAINER (array_container_s) { int32_t cardinality; int32_t capacity; uint16_t *array; };
Array Container 是 Roaring Bitmap 初始化默认的 Container。Array Container 适合存放稀疏的数据,其内部数据结构是一个有序的 short 数组 。数组初始容量为 4,数组最大容量为 4096,存储元素始终有序,方便二分查找,查询复杂度O(logn)
2、BitmapContainer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 enum { BITSET_CONTAINER_SIZE_IN_WORDS = (1 << 16 ) / 64 , BITSET_UNKNOWN_CARDINALITY = -1 }; STRUCT_CONTAINER (bitset_container_s) { int32_t cardinality; uint64_t *words; };
BitmapContainer采用long数组 存储低16位数据,这就是一个未压缩的普通Bitmap,每一个bit位置代表一个数字。每一个Container最多可以处理216 个数字,基于位图的原理需要216 个bit,每个long是8字节64bit,所以数组大小是216 /64=1024,始终占据8kb 的空间,查询复杂度O(1)
3、RunContainer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 struct rle16_s { uint16_t value; uint16_t length; }; STRUCT_CONTAINER (run_container_s) { int32_t n_runs; int32_t capacity; rle16_t *runs; };
主要解决了连续1的情况,例如15、16、17、18可以被优化成15,3。RunContainer中的关键变量为value,length,类型是short。其中,value是具体数值,length为value往后的连续个数。
例如:3,4,5,10,20,21,22,23这样一组数据会被优化成3,2,10,0,20,3,原理就是记录初始数字以及连续的数量,并把压缩后的数据记录在short数组中。这种压缩方式对于数据的疏密程度非常敏感,举两个最极端的例子:如果这个Container中所有数据都是连续的,也就是[0,1,2…..65535],压缩后为0,65535,即2个short,4字节。若这个container中所有数据都是间断的(都是偶数或奇数),也就是[0,2,4,6….65532,65534],压缩后为0,0,2,0…..65534,0,这不仅没有压缩反而膨胀了一倍,65536个short,即128kb
因此是否选择RunContainer是需要判断的,RBM提供了一个转化方法runOptimize() 用于对比和其他两种Container的空间大小,若占据优势则会进行转化。
各个Container之间比较如下 :
1. 读取时间
只有BitmapContainer可根据下标直接寻址,复杂度为O(1),ArrayContainer和RunContainer都需要二分查找,复杂度O(log n)
2. 内存占用
RoaringBitmap源码分析 CRoaring源码:https://github.com/RoaringBitmap/CRoaring
1、Add Add大致流程:
二分判断新加的Value的高16位是否存在,不存在新建一个ArrayContainer,然后添加低16位数值即可
若存在,确定低16位Container位置后,判断对应Container的类型:
Array Container:
通过二分查找Value低16位所在的ArrayContainer中的位置,若存在说明已经添加了则不处理
不存在则对元素容量Cardinality进行判断,决定是否需要扩容或者升级为BitmapContainer
将ArrayContainer中insert_idx之后的子数组后移一位,将数据插入,形成新的Array数组
Bitmap Container
低16位Add Array Container Add 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 static inline int array_container_try_add (array_container_t *arr, uint16_t value, int32_t max_cardinality) const int32_t cardinality = arr->cardinality; if ((array_container_empty (arr) || arr->array[cardinality - 1 ] < value) && cardinality < max_cardinality) { array_container_append (arr, value); return 1 ; } const int32_t loc = binarySearch (arr->array, cardinality, value); if (loc >= 0 ) { return 0 ; } else if (cardinality < max_cardinality) { if (array_container_full (arr)) { array_container_grow (arr, arr->capacity + 1 , true ); } const int32_t insert_idx = -loc - 1 ; memmove (arr->array + insert_idx + 1 , arr->array + insert_idx, (cardinality - insert_idx) * sizeof (uint16_t )); arr->array[insert_idx] = value; arr->cardinality++; return 1 ; } else { return -1 ; } }
add流程:
通过二分查找找到val所在的array中的位置,若存在则不处理,不存在则进入下一步。
对cardinality进行判断,决定是否需要升级为BitmapContainer或者扩容。
将array中insert_idx之后的子数组后移一位,将数据插入,形成新的Array数组。
Bitmap Container Add 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 bitset_container_t *bitset_container_from_array (const array_container_t *ac) bitset_container_t *ans = bitset_container_create (); int limit = array_container_cardinality (ac); for (int i = 0 ; i < limit; ++i) bitset_container_set (ans, ac->array[i]); return ans; } ... static inline void bitset_container_set (bitset_container_t *bitset, uint16_t pos) uint64_t shift = 6 ; uint64_t offset; uint64_t p = pos; ASM_SHIFT_RIGHT (p, shift, offset); uint64_t load = bitset->words[offset]; ASM_SET_BIT_INC_WAS_CLEAR (load, p, bitset->cardinality); bitset->words[offset] = load; } static inline bool bitset_container_add (bitset_container_t *bitset, uint16_t pos) const uint64_t old_word = bitset->words[pos >> 6 ]; const int index = pos & 63 ; const uint64_t new_word = old_word | (UINT64_C (1 ) << index); const uint64_t increment = (old_word ^ new_word) >> index; bitset->cardinality += (uint32_t )increment; bitset->words[pos >> 6 ] = new_word; return increment > 0 ; }
add流程:
通过pos/64找到bitmap中的long数组中的位置得到原值old_word。
old_word | (1 << (pos%64) ) 得到new_word。
改变cardinality。
2、And And流程:
获取high_low_container,判断keys数组中元素是否相等,即判断高16位
在高16位元素相等的情况下,去判断对应Container中存储的低16位元素:
Bitmap Container & Bitmap Container
快速获取两个Bitmap求交后的元素个数(底层AVX2指令集优化)
若求交后元素个数大于4096,用Bitmap Container存储,否则用Array Container存储。
Array Container & Array Container
计算结果集的cardinality的上限,并初始化
两个Array Container元素相差较大,差距大于64倍的时候,会调用intersect_skewed_uint16,步长为2的幂次方的形式递增,加速跳过不相交的元素。如果相差不大的时候,调用intersect_uint16步长为1进行比较(底层就是两个有序数组求交集) 或者intersect_vector16进行AVX2指令集加速
Bitmap Container & Array Container
给结果数组dst申请扩容,初始长度为Array Container的array的长度
for循环遍历Array Container,依次其中的元素是否在Bitmap Container中存在,如果存在的话,则更新到结果answer中,并更新Cardinality。
Array Container & Bitmap Container
高16位 And 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 roaring_bitmap_t *roaring_bitmap_and (const roaring_bitmap_t *x1, const roaring_bitmap_t *x2) uint8_t result_type = 0 ; const int length1 = x1->high_low_container.size, length2 = x2->high_low_container.size; uint32_t neededcap = length1 > length2 ? length2 : length1; roaring_bitmap_t *answer = roaring_bitmap_create_with_capacity (neededcap); roaring_bitmap_set_copy_on_write (answer, is_cow (x1) && is_cow (x2)); int pos1 = 0 , pos2 = 0 ; while (pos1 < length1 && pos2 < length2) { const uint16_t s1 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x1->high_low_container, pos1); const uint16_t s2 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x2->high_low_container, pos2); if (s1 == s2) { uint8_t type1, type2; container_t *c1 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x1->high_low_container, pos1, &type1); container_t *c2 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x2->high_low_container, pos2, &type2); container_t *c = container_and (c1, type1, c2, type2, &result_type); if (container_nonzero_cardinality (c, result_type)) { ra_append (&answer->high_low_container, s1, c, result_type); } else { container_free (c, result_type); } ++pos1; ++pos2; } else if (s1 < s2) { pos1 = ra_advance_until (&x1->high_low_container, s2, pos1); } else { pos2 = ra_advance_until (&x2->high_low_container, s1, pos2); } } return answer; }
低16位And 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 static inline container_t *container_and ( const container_t *c1, uint8_t type1, const container_t *c2, uint8_t type2, uint8_t *result_type ) c1 = container_unwrap_shared (c1, &type1); c2 = container_unwrap_shared (c2, &type2); container_t *result = NULL ; switch (PAIR_CONTAINER_TYPES (type1, type2)) { case CONTAINER_PAIR (BITSET,BITSET) : *result_type = bitset_bitset_container_intersection ( const_CAST_bitset (c1), const_CAST_bitset (c2), &result) ? BITSET_CONTAINER_TYPE : ARRAY_CONTAINER_TYPE; return result; case CONTAINER_PAIR (ARRAY,ARRAY) : result = array_container_create (); array_container_intersection (const_CAST_array (c1), const_CAST_array (c2), CAST_array (result)); *result_type = ARRAY_CONTAINER_TYPE; return result; case CONTAINER_PAIR (RUN,RUN) : result = run_container_create (); run_container_intersection (const_CAST_run (c1), const_CAST_run (c2), CAST_run (result)); return convert_run_to_efficient_container_and_free ( CAST_run (result), result_type); case CONTAINER_PAIR (BITSET,ARRAY) : result = array_container_create (); array_bitset_container_intersection (const_CAST_array (c2), const_CAST_bitset (c1), CAST_array (result)); *result_type = ARRAY_CONTAINER_TYPE; return result; case CONTAINER_PAIR (ARRAY,BITSET) : result = array_container_create (); *result_type = ARRAY_CONTAINER_TYPE; array_bitset_container_intersection (const_CAST_array (c1), const_CAST_bitset (c2), CAST_array (result)); return result; ... default : assert (false ); __builtin_unreachable(); return NULL ; } }
Bitmap Container & Bitmap Container 两个Bitmap Container求And流程:
快速获取两个Bitmap求交后的元素个数
若求交后元素个数大于4096,用Bitmap Container存储,否则用Array Container存储。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 bool bitset_bitset_container_intersection ( const bitset_container_t *src_1, const bitset_container_t *src_2, container_t **dst ) const int newCardinality = bitset_container_and_justcard (src_1, src_2); if (newCardinality > DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE) { *dst = bitset_container_create (); if (*dst != NULL ) { bitset_container_and_nocard (src_1, src_2, CAST_bitset (*dst)); CAST_bitset (*dst)->cardinality = newCardinality; } return true ; } *dst = array_container_create_given_capacity (newCardinality); if (*dst != NULL ) { CAST_array (*dst)->cardinality = newCardinality; bitset_extract_intersection_setbits_uint16 ( src_1->words, src_2->words, BITSET_CONTAINER_SIZE_IN_WORDS, CAST_array (*dst)->array, 0 ); } return false ; } size_t bitset_extract_intersection_setbits_uint16 (const uint64_t * __restrict__ words1, const uint64_t * __restrict__ words2, size_t length, uint16_t *out, uint16_t base) int outpos = 0 ; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < length; ++i) { uint64_t w = words1[i] & words2[i]; while (w != 0 ) { uint64_t t = w & (~w + 1 ); int r = __builtin_ctzll(w); out[outpos++] = r + base; w ^= t; } base += 64 ; } return outpos; }
Array Container & Array Container 两个Array Container求And流程:
首先计算结果集的cardinality的上限,并初始化
两个Array Container元素相差较大,差距大于64倍的时候,会调用intersect_skewed_uint16,步长为2的幂次方的形式递增,加速跳过不相交的元素。如果相差不大的时候,调用intersect_uint16步长为1进行比较(底层就是两个有序数组求交集) 或者intersect_vector16进行avx2指令集加速。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 void array_container_intersection (const array_container_t *array1, const array_container_t *array2, array_container_t *out) int32_t card_1 = array1->cardinality, card_2 = array2->cardinality, min_card = minimum_int32 (card_1, card_2); const int threshold = 64 ; #ifdef CROARING_IS_X64 if (out->capacity < min_card) { array_container_grow (out, min_card + sizeof (__m128i) / sizeof (uint16_t ), false ); } #else if (out->capacity < min_card) { array_container_grow (out, min_card, false ); } #endif if (card_1 * threshold < card_2) { out->cardinality = intersect_skewed_uint16 ( array1->array, card_1, array2->array, card_2, out->array); } else if (card_2 * threshold < card_1) { out->cardinality = intersect_skewed_uint16 ( array2->array, card_2, array1->array, card_1, out->array); } else { #ifdef CROARING_IS_X64 if ( croaring_avx2 () ) { out->cardinality = intersect_vector16 ( array1->array, card_1, array2->array, card_2, out->array); } else { out->cardinality = intersect_uint16 (array1->array, card_1, array2->array, card_2, out->array); } #else out->cardinality = intersect_uint16 (array1->array, card_1, array2->array, card_2, out->array); #endif } }
Bitmap Container & Array Container Bitmap Container 和 Array Container And流程:
首先,给dst申请扩容,初始长度为ArrayContainer的array的长度
然后for循环遍历ArrayContainer,依次其中的元素是否在BitmapContainer中存在,如果存在的话,则更新到结果answer中,并增加cardinality。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 void array_bitset_container_intersection (const array_container_t *src_1, const bitset_container_t *src_2, array_container_t *dst) if (dst->capacity < src_1->cardinality) { array_container_grow (dst, src_1->cardinality, false ); } int32_t newcard = 0 ; const int32_t origcard = src_1->cardinality; for (int i = 0 ; i < origcard; ++i) { uint16_t key = src_1->array[i]; dst->array[newcard] = key; newcard += bitset_container_contains (src_2, key); } dst->cardinality = newcard; }
Array Container & Bitmap Container 同上Bitmap Container & Array Container的原理。
同时还有iand,标识inplace的And操作,原理与上述基本类似。
3、Or Or流程:
获取high_low_container,while循环遍历判断keys数组中元素,在高16位相等的情况下,调用container_or求两个container的并集
Bitmap Container | Bitmap Container
两个Bitmap求并集(底层使用AVX2指令集加速批量处理)
Array Container | Array Container
预估取并集后的元素个数是否小于4096,
是,则新建一个Array Container
否,则新建一个Bitmap Container
Bitmap Container | Array Container
Copy一份Bitmap Container
遍历Array Container的元素,添加进新的Bitmap Container
Array Container | Bitmap Container
高16位元素不相等,直接给answer添加对应的key及container
高16位 or 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 roaring_bitmap_t *roaring_bitmap_or (const roaring_bitmap_t *x1, const roaring_bitmap_t *x2) uint8_t result_type = 0 ; const int length1 = x1->high_low_container.size, length2 = x2->high_low_container.size; if (0 == length1) { return roaring_bitmap_copy (x2); } if (0 == length2) { return roaring_bitmap_copy (x1); } roaring_bitmap_t *answer = roaring_bitmap_create_with_capacity (length1 + length2); roaring_bitmap_set_copy_on_write (answer, is_cow (x1) && is_cow (x2)); int pos1 = 0 , pos2 = 0 ; uint8_t type1, type2; uint16_t s1 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x1->high_low_container, pos1); uint16_t s2 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x2->high_low_container, pos2); while (true ) { if (s1 == s2) { container_t *c1 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x1->high_low_container, pos1, &type1); container_t *c2 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x2->high_low_container, pos2, &type2); container_t *c = container_or (c1, type1, c2, type2, &result_type); ra_append (&answer->high_low_container, s1, c, result_type); ++pos1; ++pos2; if (pos1 == length1) break ; if (pos2 == length2) break ; s1 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x1->high_low_container, pos1); s2 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x2->high_low_container, pos2); } else if (s1 < s2) { container_t *c1 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x1->high_low_container, pos1, &type1); c1 = get_copy_of_container (c1, &type1, is_cow (x1)); if (is_cow (x1)) { ra_set_container_at_index (&x1->high_low_container, pos1, c1, type1); } ra_append (&answer->high_low_container, s1, c1, type1); pos1++; if (pos1 == length1) break ; s1 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x1->high_low_container, pos1); } else { container_t *c2 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x2->high_low_container, pos2, &type2); c2 = get_copy_of_container (c2, &type2, is_cow (x2)); if (is_cow (x2)) { ra_set_container_at_index (&x2->high_low_container, pos2, c2, type2); } ra_append (&answer->high_low_container, s2, c2, type2); pos2++; if (pos2 == length2) break ; s2 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x2->high_low_container, pos2); } } if (pos1 == length1) { ra_append_copy_range (&answer->high_low_container, &x2->high_low_container, pos2, length2, is_cow (x2)); } else if (pos2 == length2) { ra_append_copy_range (&answer->high_low_container, &x1->high_low_container, pos1, length1, is_cow (x1)); } return answer; }
低16位 Container Or 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 static inline container_t *container_or ( const container_t *c1, uint8_t type1, const container_t *c2, uint8_t type2, uint8_t *result_type ) c1 = container_unwrap_shared (c1, &type1); c2 = container_unwrap_shared (c2, &type2); container_t *result = NULL ; switch (PAIR_CONTAINER_TYPES (type1, type2)) { case CONTAINER_PAIR (BITSET,BITSET) : result = bitset_container_create (); bitset_container_or (const_CAST_bitset (c1), const_CAST_bitset (c2), CAST_bitset (result)); *result_type = BITSET_CONTAINER_TYPE; return result; case CONTAINER_PAIR (ARRAY,ARRAY) : // 2 、两个Array Container求or *result_type = array_array_container_union ( const_CAST_array (c1), const_CAST_array (c2), &result) ? BITSET_CONTAINER_TYPE : ARRAY_CONTAINER_TYPE; return result; case CONTAINER_PAIR (RUN,RUN) : // 3 、两个Run Container求or result = run_container_create (); run_container_union (const_CAST_run (c1), const_CAST_run (c2), CAST_run (result)); *result_type = RUN_CONTAINER_TYPE; result = convert_run_to_efficient_container_and_free ( CAST_run (result), result_type); return result; case CONTAINER_PAIR (BITSET,ARRAY) : result = bitset_container_create (); array_bitset_container_union (const_CAST_array (c2), const_CAST_bitset (c1), CAST_bitset (result)); *result_type = BITSET_CONTAINER_TYPE; return result; case CONTAINER_PAIR (ARRAY,BITSET) : result = bitset_container_create (); array_bitset_container_union (const_CAST_array (c1), const_CAST_bitset (c2), CAST_bitset (result)); *result_type = BITSET_CONTAINER_TYPE; return result; ... default : assert (false ); __builtin_unreachable(); return NULL ; } }
两个Array Container求Or 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 bool array_array_container_union ( const array_container_t *src_1, const array_container_t *src_2, container_t **dst ) int totalCardinality = src_1->cardinality + src_2->cardinality; if (totalCardinality <= DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE) { *dst = array_container_create_given_capacity (totalCardinality); if (*dst != NULL ) { array_container_union (src_1, src_2, CAST_array (*dst)); } else { return true ; } return false ; } *dst = bitset_container_create (); bool returnval = true ; if (*dst != NULL ) { bitset_container_t *ourbitset = CAST_bitset (*dst); bitset_set_list (ourbitset->words, src_1->array, src_1->cardinality); ourbitset->cardinality = (int32_t )bitset_set_list_withcard ( ourbitset->words, src_1->cardinality, src_2->array, src_2->cardinality); if (ourbitset->cardinality <= DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE) { *dst = array_container_from_bitset (ourbitset); bitset_container_free (ourbitset); returnval = false ; } } return returnval; }
Array Container 和 Bitmap Container求 Or 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 void array_bitset_container_union (const array_container_t *src_1, const bitset_container_t *src_2, bitset_container_t *dst) if (src_2 != dst) bitset_container_copy (src_2, dst); dst->cardinality = (int32_t )bitset_set_list_withcard ( dst->words, dst->cardinality, src_1->array, src_1->cardinality); } ... uint64_t bitset_set_list_withcard (uint64_t *words, uint64_t card, const uint16_t *list, uint64_t length) uint64_t offset, load, newload, pos, index; const uint16_t *end = list + length; while (list != end) { pos = *list; offset = pos >> 6 ; index = pos % 64 ; load = words[offset]; newload = load | (UINT64_C (1 ) << index); card += (load ^ newload) >> index; words[offset] = newload; list++; } return card; }
4、FastUnion 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 static Roaring fastunion (size_t n, const Roaring **inputs) const roaring_bitmap_t **x = (const roaring_bitmap_t **)malloc (n * sizeof (roaring_bitmap_t *)); if (x == NULL ) { ROARING_TERMINATE ("failed memory alloc in fastunion" ); } for (size_t k = 0 ; k < n; ++k) x[k] = &inputs[k]->roaring; roaring_bitmap_t *c_ans = api::roaring_bitmap_or_many (n, x); if (c_ans == NULL ) { free (x); ROARING_TERMINATE ("failed memory alloc in fastunion" ); } Roaring ans (c_ans) ; free (x); return ans; } ... roaring_bitmap_t *roaring_bitmap_or_many (size_t number, const roaring_bitmap_t **x) if (number == 0 ) { return roaring_bitmap_create (); } if (number == 1 ) { return roaring_bitmap_copy (x[0 ]); } roaring_bitmap_t *answer = roaring_bitmap_lazy_or (x[0 ], x[1 ], LAZY_OR_BITSET_CONVERSION); for (size_t i = 2 ; i < number; i++) { roaring_bitmap_lazy_or_inplace (answer, x[i], LAZY_OR_BITSET_CONVERSION); } roaring_bitmap_repair_after_lazy (answer); return answer; } ... roaring_bitmap_t *roaring_bitmap_lazy_or (const roaring_bitmap_t *x1, const roaring_bitmap_t *x2, const bool bitsetconversion) uint8_t result_type = 0 ; const int length1 = x1->high_low_container.size, length2 = x2->high_low_container.size; if (0 == length1) { return roaring_bitmap_copy (x2); } if (0 == length2) { return roaring_bitmap_copy (x1); } roaring_bitmap_t *answer = roaring_bitmap_create_with_capacity (length1 + length2); roaring_bitmap_set_copy_on_write (answer, is_cow (x1) && is_cow (x2)); int pos1 = 0 , pos2 = 0 ; uint8_t type1, type2; uint16_t s1 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x1->high_low_container, pos1); uint16_t s2 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x2->high_low_container, pos2); while (true ) { if (s1 == s2) { container_t *c1 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x1->high_low_container, pos1, &type1); container_t *c2 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x2->high_low_container, pos2, &type2); container_t *c; if (bitsetconversion && (get_container_type (c1, type1) != BITSET_CONTAINER_TYPE) && (get_container_type (c2, type2) != BITSET_CONTAINER_TYPE) ){ container_t *newc1 = container_mutable_unwrap_shared (c1, &type1); newc1 = container_to_bitset (newc1, type1); type1 = BITSET_CONTAINER_TYPE; c = container_lazy_ior (newc1, type1, c2, type2, &result_type); if (c != newc1) { container_free (newc1, type1); } } else { c = container_lazy_or (c1, type1, c2, type2, &result_type); } ra_append (&answer->high_low_container, s1, c, result_type); ++pos1; ++pos2; if (pos1 == length1) break ; if (pos2 == length2) break ; s1 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x1->high_low_container, pos1); s2 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x2->high_low_container, pos2); } else if (s1 < s2) { container_t *c1 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x1->high_low_container, pos1, &type1); c1 = get_copy_of_container (c1, &type1, is_cow (x1)); if (is_cow (x1)) { ra_set_container_at_index (&x1->high_low_container, pos1, c1, type1); } ra_append (&answer->high_low_container, s1, c1, type1); pos1++; if (pos1 == length1) break ; s1 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x1->high_low_container, pos1); } else { container_t *c2 = ra_get_container_at_index ( &x2->high_low_container, pos2, &type2); c2 = get_copy_of_container (c2, &type2, is_cow (x2)); if (is_cow (x2)) { ra_set_container_at_index (&x2->high_low_container, pos2, c2, type2); } ra_append (&answer->high_low_container, s2, c2, type2); pos2++; if (pos2 == length2) break ; s2 = ra_get_key_at_index (&x2->high_low_container, pos2); } } if (pos1 == length1) { ra_append_copy_range (&answer->high_low_container, &x2->high_low_container, pos2, length2, is_cow (x2)); } else if (pos2 == length2) { ra_append_copy_range (&answer->high_low_container, &x1->high_low_container, pos1, length1, is_cow (x1)); } return answer; }
EXPERIMENTS 参考论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1709.07821.pdf
内存使用:
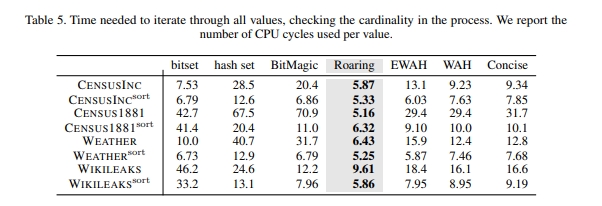
遍历一遍所使用的耗时:
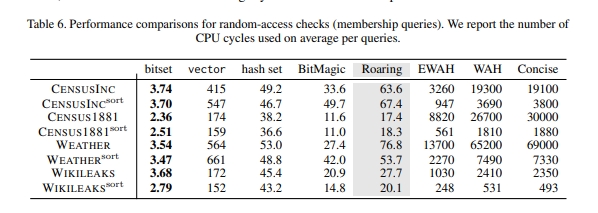
随机获取某个元素的耗时:
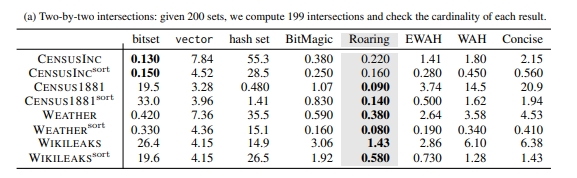
两两求交集:
两两求并集:
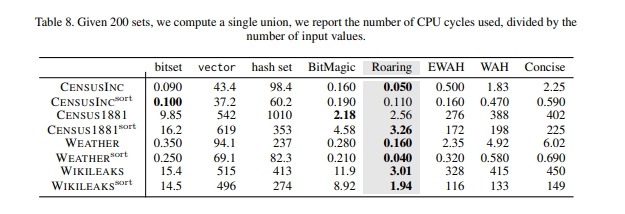
多个集合求并集:
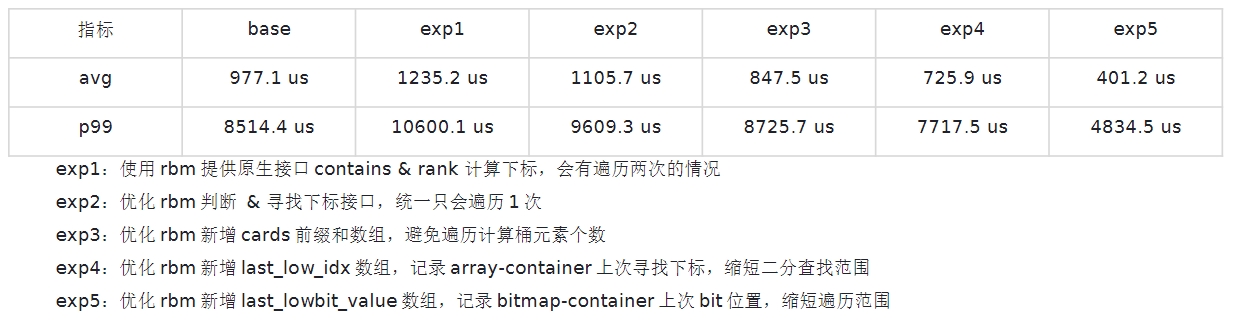
RoaringBitmap优化寻址 利用 RBM 结构特性去计算某个 doc 对应的下标,即计算某个数是 RBM 中的第几个 1,在此基础上我针对CRoaring源码实现部分,做了一些小小的优化,现将优化思路简单分享一下。
CRoaring原生的提供两个接口contains 和 rank,一个是判断某个数是否存在,一个是计算集合中小于等于某个数的个数,接口函数代码如下:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 bool contains (uint32_t x) const noexcept return api::roaring_bitmap_contains (&roaring, x); } uint64_t rank (uint32_t x) const noexcept return api::roaring_bitmap_rank (&roaring, x); }
针对一些数据,写了一个benchmark的工具
核心的优化思路是充分利用LocalDocID的有序性,尽可能缓存上一次的计算结果,减少重复计算。
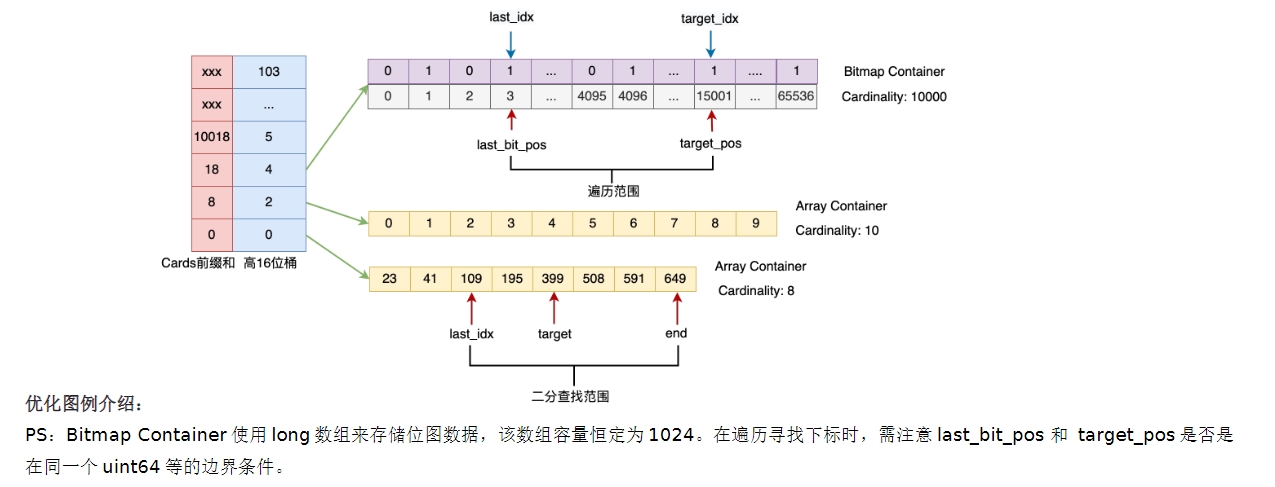
优化图例介绍:
其中 exp2的这部分的寻址优化工作也向CRoaring开源库提交一次PR ,已由开源项目维护者审核通过并发布。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 int64_t getIndex (uint32_t x) const noexcept return api::roaring_bitmap_get_index (&roaring, x); }